Homework Help Overview
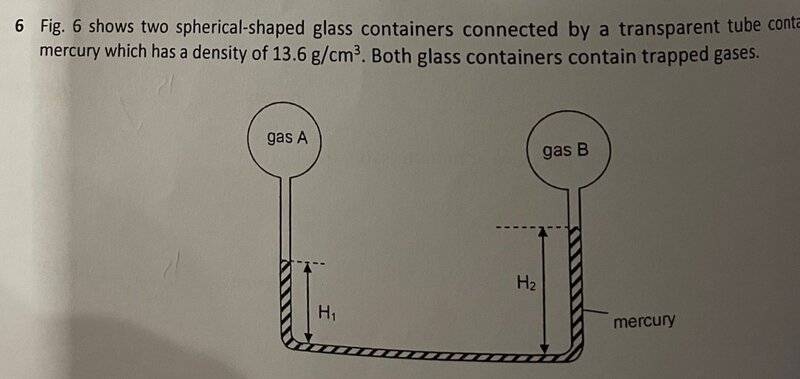
The discussion revolves around a question regarding the pressure difference between two gases in a static system, specifically focusing on the interpretation of pressure readings and the implications of a teacher's response to a student's reasoning.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Assumption checking, Conceptual clarification
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants discuss the relationship between gas pressure and mercury levels in a manometer setup, questioning the validity of the teacher's assertion that one gas has a higher pressure than the other. Some participants present their reasoning based on hydrostatic principles, while others reflect on the social dynamics of challenging authority in an educational setting.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with various perspectives being shared. Some participants express a desire for open dialogue with the teacher, while others caution against public challenges. There is a mix of support for questioning the teacher and concern for maintaining classroom harmony.
Contextual Notes
There is a noted tension between the student's understanding of the physics involved and the teacher's explanation, which has not been elaborated upon. The participants are navigating the complexities of classroom dynamics and the implications of questioning a teacher's authority.