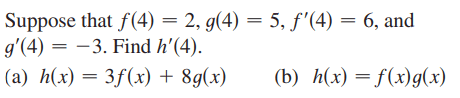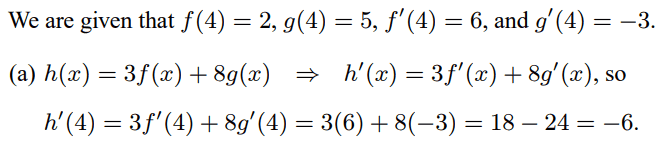SUMMARY
The discussion clarifies why the chain rule is not applicable in differentiating the function h(x) = 3f(x) + 8g(x). The key point is that both f(x) and g(x) are direct functions of x without any inner functions, making the chain rule unnecessary. Instead, the derivative h'(x) is computed using the sum rule and constant multiple rules, resulting in h'(x) = 3f'(x) + 8g'(x). This approach allows for straightforward calculation of h'(4) without involving inner functions.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of basic differentiation rules, including the sum rule and constant multiple rule.
- Familiarity with function notation and derivatives.
- Knowledge of composite functions and the chain rule in calculus.
- Ability to evaluate derivatives at specific points, such as h'(4).
NEXT STEPS
- Review the sum rule and constant multiple rule in differentiation.
- Study the chain rule and its application in differentiating composite functions.
- Practice differentiating various functions, including trigonometric and polynomial functions.
- Explore examples of functions with inner functions to understand when to apply the chain rule.
USEFUL FOR
Students learning calculus, particularly those focusing on differentiation techniques, as well as educators seeking to clarify common misconceptions about the chain rule and its applications.