- #1
DottZakapa
- 239
- 17
- Homework Statement
- compute the double integral
- Relevant Equations
- double integral
D={(x,y)∈ℝ2: 2|y|-2≤|x|≤½|y|+1}
I am struggling on finding the domain of such function
my attempt :
first system
\begin{cases}
x≥2y-2\\
-x≥2y-2\\
x≥-2y-2\\
-x≥-2y-2
\end{cases}
second system
\begin{cases}
x≤y/2+1\\
x≤-y/2+1\\
-x≤y/2+1\\
-x≤-y/2+1\\
\end{cases}
i draw the graph and get the intersection for each system, then intersect the two graphs?
first system
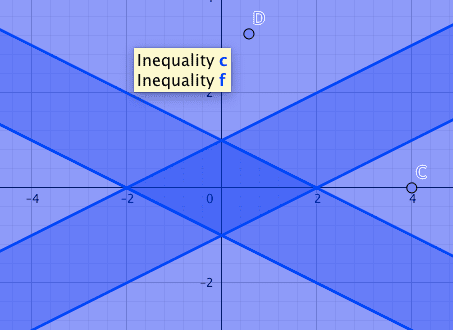
Second
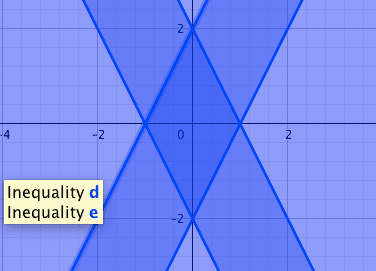
intersection between the two
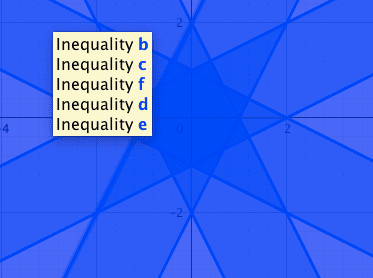
is the procedure correct or in what am i doing wrong?
I am struggling on finding the domain of such function
my attempt :
first system
\begin{cases}
x≥2y-2\\
-x≥2y-2\\
x≥-2y-2\\
-x≥-2y-2
\end{cases}
second system
\begin{cases}
x≤y/2+1\\
x≤-y/2+1\\
-x≤y/2+1\\
-x≤-y/2+1\\
\end{cases}
i draw the graph and get the intersection for each system, then intersect the two graphs?
first system
Second
intersection between the two
is the procedure correct or in what am i doing wrong?