- #1
sep1231
- 1
- 0
- Homework Statement
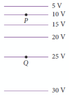
- In the figure (attached), the lines represent equipotential lines. A positive point charge is placed at point P, and another positive point charge is placed at Q. Which set of vectors represent the relative magnitudes and directions of the electric field exerted on the positive charges at P and Q?
a) Equal fields directed from P to Q
b) Field in P greater than in Q, directed from Q to P
c) Field in P smaller than in Q, directed from Q to P
d) Field in P greater than in Q, directed from P to Q
e) Field in P smaller than in Q, directed from P to Q
- Relevant Equations
- E = -V/d
I know that the electric field is directed from Q to P, but I'm not sure which magnitud is greater, I tried this