- #1
Morbidly_Green
- 12
- 0
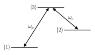
Homework Statement
Given the above lambda system, is it wrong to say that the density matrix is of the form ## \rho = c_1|1> + c_2|2> + c_3|3> ## ? Hence when written in matrix form (basis of ##|i>##), ## \rho ## is a diagonal matrix who's elements are the ##c_i##s?