- #1
LCSphysicist
- 645
- 161
- Homework Statement
- Latitude can be measured with a gyro by mounting the gyro with
its axle horizontal and lying along the east·west axis.
a. Show that the gyro can remain stationary when its spin axis is
parallel to the polar axis and is at the latitude angle A with the horizontal.
- Relevant Equations
- fg = mg
t = rf
l = Io*w
I am not sure about a, but i think as long as there is no torque about the Lp direction, it will remain constant with relation to the polar star. I would like help in proof this mathematically.
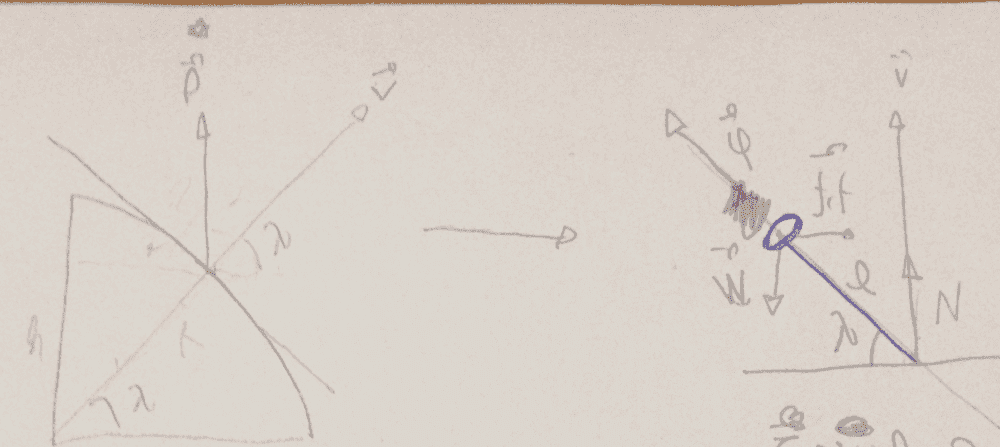
I just don't know how to proceed, i wonder if i would need to consider the torque provide by Centrifuge and Coriolis force, well... It made me wonder if I'm really on the right track.
p is a vector pointing polar star
v is a vertical vector.
Lambda is latitude
W is weight
fcf is force centrifuge
N is reaction in a pivot
I just don't know how to proceed, i wonder if i would need to consider the torque provide by Centrifuge and Coriolis force, well... It made me wonder if I'm really on the right track.
p is a vector pointing polar star
v is a vertical vector.
Lambda is latitude
W is weight
fcf is force centrifuge
N is reaction in a pivot