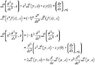- #1
starzero
- 20
- 0
In my differential equations book (Edward and Penny) there are many examples of Laplace transforms being applied to linear differential equations with constant coefficients and no examples of them being applied to linear differential equations with variable coefficients. My question is, can this be done?
In particular, can someone take the Laplace Transform of something like
x^2 (d^2/dx^2)
If the answer is yes, can you provide me with a reference?
For the most part when the equations have variable coefficients the only methods that I have seen are series methods and substitution methods.
Thanks in advance for reading and any response.
In particular, can someone take the Laplace Transform of something like
x^2 (d^2/dx^2)
If the answer is yes, can you provide me with a reference?
For the most part when the equations have variable coefficients the only methods that I have seen are series methods and substitution methods.
Thanks in advance for reading and any response.