- #1
SpaceGuy
- 20
- 0
I heard about a technique where mercury or some other liquid is spun in a dish until it assumes a parabolic shape. Would this work in space? Could a flat membrane of liquid metal do just as well? It could be liquified by an electric current and start out flat like soapy water in a bubble wand.

If we then spun the ring and accelerated the whole thing along at 1 g to simulate gravity could it assume a parabolic shape? If so then switching of the electric current could preserve it as it cools and solidifies. I'm wondering if this might also work with spinning bubbles. Couldn't we then make incredibly thin yet huge reflector mirrors in space well beyond the influence of gravity?
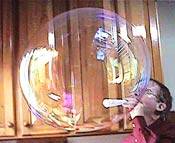
Ordinary metal might not be elastic enough to make bubbles out of. Water isn't flexible enough to hold the air. It requires soap before a thin film of the liquid can be made to surround a pocket of air. In space there is no air at all so bubbles might only form in a pressurised cabin area. I don't know if a bubble could hold shape with air inside it and vacuum outside but would be interested in knowing.

http://www.ironworks.com/westham/larson.gif
If we then spun the ring and accelerated the whole thing along at 1 g to simulate gravity could it assume a parabolic shape? If so then switching of the electric current could preserve it as it cools and solidifies. I'm wondering if this might also work with spinning bubbles. Couldn't we then make incredibly thin yet huge reflector mirrors in space well beyond the influence of gravity?
Ordinary metal might not be elastic enough to make bubbles out of. Water isn't flexible enough to hold the air. It requires soap before a thin film of the liquid can be made to surround a pocket of air. In space there is no air at all so bubbles might only form in a pressurised cabin area. I don't know if a bubble could hold shape with air inside it and vacuum outside but would be interested in knowing.
http://www.ironworks.com/westham/larson.gif
Last edited by a moderator: