- #1
ace8888
- 19
- 0
< Mentor Note -- thread moved to HH from the technical physics forums, so no HH Template is shown >
Hi,
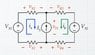
I couldn't figure out from the equation that relate the current source IS to IA and IB. If both IA and IB is coming from the same direction and the positive terminal has been predicted. Wouldnt that be IA + IB = IS?
The solution is IA + IB = -IS. Is the negative comes from the current source actual direction is the opposite of what was predicted, which was positive at the top and negative at the bottom ?
thanks
Hi,
I couldn't figure out from the equation that relate the current source IS to IA and IB. If both IA and IB is coming from the same direction and the positive terminal has been predicted. Wouldnt that be IA + IB = IS?
The solution is IA + IB = -IS. Is the negative comes from the current source actual direction is the opposite of what was predicted, which was positive at the top and negative at the bottom ?
thanks
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: