- #1
Scienceklutz
- 3
- 0
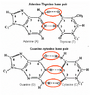
The question: What happens to the extra hydrogen when the base pairs combine?
For example the formula for Adenine and Thymine are C5H5N5 & C5H6N2O2. So when combined there should be 11 hydrogen, however in the diagrams for A and T when together only show H9. 2 off. Same with G and C, C5H5N5O & C4H5N3O. There should be 10 hydrogen total, but the diagram shows 8. 2 off. What concept am I missing?
Thank you!
For example the formula for Adenine and Thymine are C5H5N5 & C5H6N2O2. So when combined there should be 11 hydrogen, however in the diagrams for A and T when together only show H9. 2 off. Same with G and C, C5H5N5O & C4H5N3O. There should be 10 hydrogen total, but the diagram shows 8. 2 off. What concept am I missing?
Thank you!