- #1
a1234
- 77
- 6
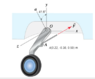
Homework Statement
I'm a bit confused on when a force creates a moment about a point, and when it does not. In particular, in the attached diagram, would F be able to produce a moment about point A? I initially thought that wouldn't be possible as A lies on the same line as F, but since F does not seem to pass directly through A, I'm not so sure.