- #1
PhysicsTest
- 238
- 26
- TL;DR Summary
- I wanted to understand how to connect the motor
This is an MCLV-2 development board from microchip, with it got the Hurst motor as shown below
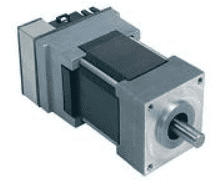
The problem is that the shaft is smooth i cannot connect the loads etc. So, I want to clarify the below points
a. What type of connectors i should look for and which websites will have the information?
b. If i want to test the performance of the motor i mean the torque, speed. Which tool do i need to buy?
Presently i have not decided the load to connect.
The problem is that the shaft is smooth i cannot connect the loads etc. So, I want to clarify the below points
a. What type of connectors i should look for and which websites will have the information?
b. If i want to test the performance of the motor i mean the torque, speed. Which tool do i need to buy?
Presently i have not decided the load to connect.
Last edited by a moderator: