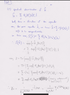- #1
alc95
- 7
- 0
Homework Statement
Homework Equations
in addition to those provided in the questions, I used the following:
Tr(B) = sigma<x_j|B|x_j>
purity = Tr(rho^2)
The Attempt at a Solution
[/B]
I find calculating trace and purity very confusing. Am I on the right track with question 1? With question 2, I am really unsure about how to proceed further. Any help would be greatly appreciated.
Thanks in advance.