- #1
Steven Bolgiano
- 43
- 3
I have in a prototype model, a pipe connected from one tank of liquid to another holding tank (at a lower a lower elevation). Its a biodigester, so the way it works is when liquid is added to tank #1, an equal amount is displaced through the pipe,
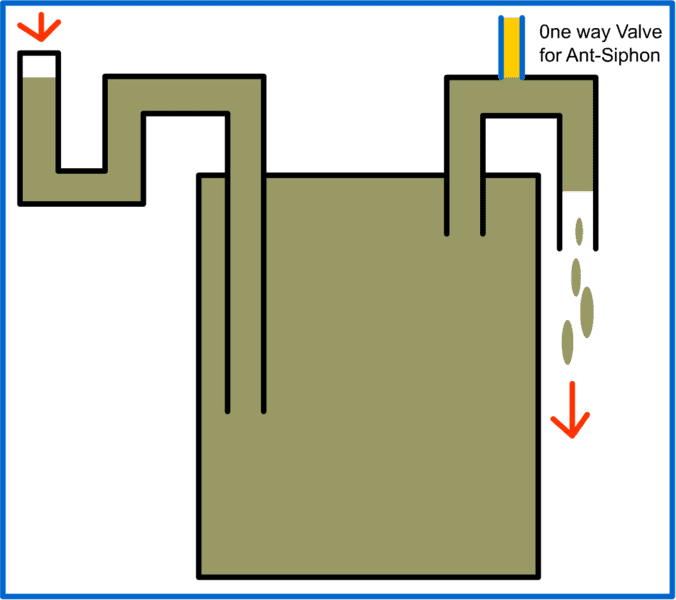

 into the lower level holding tank, #2. The concern is preventing a siphon situation where after the liquid displaces through the connecting pipe, it continues to draw liquid.
into the lower level holding tank, #2. The concern is preventing a siphon situation where after the liquid displaces through the connecting pipe, it continues to draw liquid.
A check valve in the pipe line should prevent this. But I've gone stupid on two points:
1) Which way does the check valve go? My instinct say since vacuum pressure is involved, the check valve should be placed to allow outside air into the pipe.
2) What is a definitive description of how siphons work and more importantly, WHY a siphon works?
s.
A check valve in the pipe line should prevent this. But I've gone stupid on two points:
1) Which way does the check valve go? My instinct say since vacuum pressure is involved, the check valve should be placed to allow outside air into the pipe.
2) What is a definitive description of how siphons work and more importantly, WHY a siphon works?
s.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: