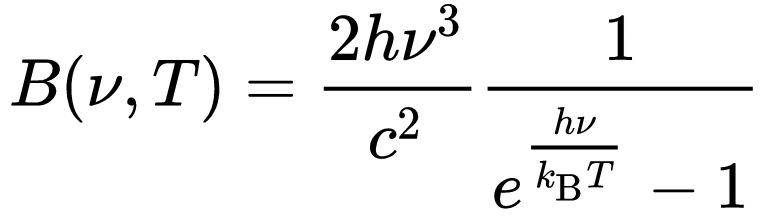- #1
Taulant Sholla
- 96
- 5
- TL;DR Summary
- Where is the quantization term (the "n") in Planck's Law?
This is a very remedial question, so thanks in advance for you gentle indulgence  Where do I find the quantization term (the "n") in Planck's Law?
Where do I find the quantization term (the "n") in Planck's Law?