- #1
SPEOTW
- 4
- 0
- TL;DR Summary
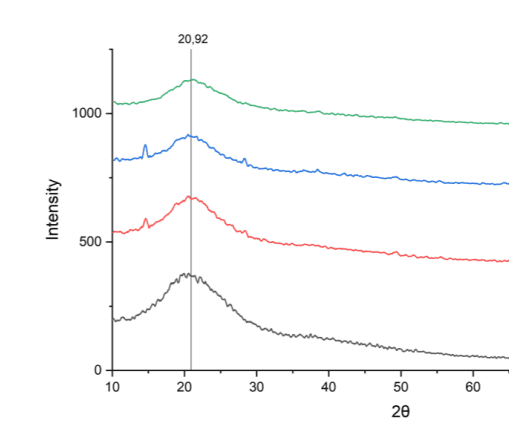
- Confusion about amorphous and crystalline region on XRD result
So i just have my XRD result (Polymer Specimen) which i use to determine crystallinity of my material, and it turns out that my material has no obvious peak, and have a broad peak which usually associated with amorphous material. I added some filler to my material and it became more and more broad but the peak stays there. does it mean my material become "more amorphous" or what does it mean