You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
2 wires attached to another wire attached to a block
- Thread starter random124
- Start date
AI Thread Summary
The discussion centers on understanding why the weight of a suspended object is equal to the tension in the cord (Tension C) supporting it. The object is not accelerating, indicating that the net force acting on it is zero. This balance of forces means that the gravitational force (weight) acting downward is countered by the tension in the cord acting upward. The presence of additional cords does not affect the forces acting directly on the suspended object, which only experiences gravity and the tension from the cord. Ultimately, the tension in the cord equals the weight of the object due to this equilibrium of forces.
Physics news on Phys.org
- 19,358
- 15,542
Draw a force diagram
- 42,673
- 10,442
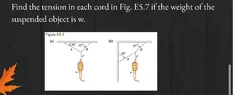
What forces act on the suspended object? Is the suspended object accelerating?random124 said:Homework Statement: Why is the weight equal to the tension of C?
Relevant Equations: Fg = Tc
Why is the weight equal to the tension of C?
The "relevant equations" item in the template is for standard equations, such as Newton’s laws, that would be relevant to the question. Which of those relates forces on a body to its acceleration?
random124
- 4
- 1
the object has no acceleration its suspended.
- 19,358
- 15,542
Draw a force diagram
- 42,673
- 10,442
So what does that tell you about the net force acting on it?random124 said:the object has no acceleration its suspended.
And what forces contribute to that total?
random124
- 4
- 1
That the net force is 0 but I don't understand why is the weight and tension of the cord that's pushing the weight up equal if there are other cords attached
- 42,673
- 10,442
The other cords are not attached to the weight.random124 said:That the net force is 0 but I don't understand why is the weight and tension of the cord that's pushing the weight up equal if there are other cords attached
Each body only "knows" about the forces that act directly on it. The suspended body is only directly acted on by gravity and the vertical cord; that cord (taken as massless) is only acted upon by the suspended weight and the knot; the knot is acted on by three cords; etc.
If the knot were directly attached to a ceiling instead of to the upper two cords it would make no difference to anything below the knot.
- 19,358
- 15,542
DO A FORCE DIAGRAM !!!random124 said:That the net force is 0 but I don't understand why is the weight and tension of the cord that's pushing the weight up equal if there are other cords attached
Lnewqban
Homework Helper
Gold Member
- 4,074
- 2,311
Welcome!random124 said:That the net force is 0 but I don't understand why is the weight and tension of the cord that's pushing the weight up equal if there are other cords attached
When your fingers are holding a suspended bad of groceries, do they feel increased or reduced weight of the groceries?
The handles of the bag are also supporting as much weight as your fingers.
Similar threads
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 21
- Views
- 383
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 772
- Replies
- 11
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 1
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 17
- Views
- 3K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
Hot Threads
-
Torque biomechanics
- Started by Naucus
- Replies: 6
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
Work Done in slowly pulling a thread
- Started by Bling Fizikst
- Replies: 28
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
-
How do you calculate the pull of this piston?
- Started by vdance
- Replies: 27
- Introductory Physics Homework Help
Recent Insights
-
Insights Why Entangled Photon-Polarization Qubits Violate Bell’s Inequality
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 26
- Quantum Interpretations and Foundations
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 11
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 3
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 1
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 105
- General Math