- #1
peasngravy
- 72
- 6
- Homework Statement
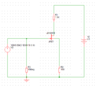
- FIGURE 4 shows an amplifier circuit. Write a short report on the
operation and performance of the circuit. In completing the report you
should:
• Explain the operation of the circuit and in particular the role of
resistors R1 and R2.
• Build the circuit in PSpice and use it to determine:
(i) the quiescent value of Vout.
(ii) the voltage gain for a 100 mV, 1 kHz , input signal.
• Sketch the small-signal equivalent circuit of the amplifier and use it
to estimate the voltage gain. Compare your answer with that of (ii)
above.
• Attempt to calculate the quiescent value of Vout. Compare your
answer with that given by the PSpice model. Try to explain any
discrepancies.
- Relevant Equations
- VGS = -IDS RS
I have calculated my own solution but I am struggling to work out how to use Pspice to compare my values. I am using simetrix for this - could anyone help with this part?
My solution is:
VGS = -IDS RS
Av = Vo/Vi
Vo= -gm VGS RL
Vi = VGS (1+gmRS)
gm= IDS/VGS so gm= IDS/-IDS RS = 1/RD = -1/100 = 0.01
so
Av = -gmRL/1+gmRS = -0.01 x 1500/1 + 0.01 x 100 = -7.5
Vo = Av x Vi = -7.5 x 0.1 = -750mV
VDS = VDD - IDS (Rd+Rs)
VD-VS = VDD - IDS Rd - IDS Rs
VD = VDD - IDS Rd
IDS = (VDD - VD)/RD = (12- (-0.75))/1500 = 8.5mA
gm = IDS/VGS, so VGS =IDS/gm = 0.0085/0.010 = 0.85V
I think that is correct, i am just not sure how to use simetrix to check it, any help would be appreciated. Thank you
My solution is:
VGS = -IDS RS
Av = Vo/Vi
Vo= -gm VGS RL
Vi = VGS (1+gmRS)
gm= IDS/VGS so gm= IDS/-IDS RS = 1/RD = -1/100 = 0.01
so
Av = -gmRL/1+gmRS = -0.01 x 1500/1 + 0.01 x 100 = -7.5
Vo = Av x Vi = -7.5 x 0.1 = -750mV
VDS = VDD - IDS (Rd+Rs)
VD-VS = VDD - IDS Rd - IDS Rs
VD = VDD - IDS Rd
IDS = (VDD - VD)/RD = (12- (-0.75))/1500 = 8.5mA
gm = IDS/VGS, so VGS =IDS/gm = 0.0085/0.010 = 0.85V
I think that is correct, i am just not sure how to use simetrix to check it, any help would be appreciated. Thank you