Dotini
Gold Member
- 634
- 231
The following article is from the January 28, 2016 edition of Spaceweather.com:
INTENSIFYING COSMIC RAYS: For the past year, neutron monitors around the Arctic Circle have sensed an increasing intensity of cosmic rays. Polar latitudes are a good place to make such measurements, because Earth's magnetic field funnels and concentrates cosmic radiation there. Turns out, Earth's poles aren't the only place cosmic rays are intensifying. Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus have been launching helium balloons to the stratosphere to measure radiation, and they find the same trend over California:
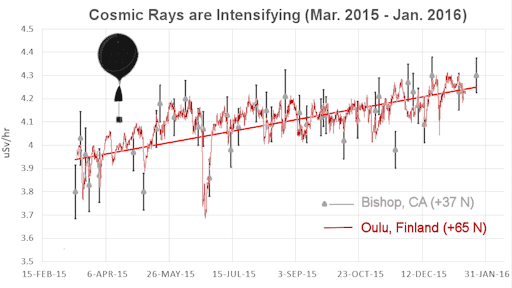
In the plot, neutron monitor measurements from the University of Oulu Cosmic Ray Station are traced in red; gamma-ray/X-ray measurements over California are denoted in gray. The agreement between the two curves is remarkable. It means that the intensification of cosmic rays is making itself felt not only over the poles, but also over lower latitudes where Earth's magnetic field provides a greater degree of protection against deep space radiation.
Cosmic rays, which are accelerated toward Earth by distant supernova explosions and other violent events, are an important form of space weather. They can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Indeed, our measurements show that someone flying back and forth across the continental USA, just once, can absorb as much ionizing cosmic radiation as 2 to 5 dental X-rays. Likewise, cosmic rays can affect mountain climbers, high-altitude drones, and astronauts onboard the International Space Station.
This type of radiation is modulated by solar activity. Solar storms and CMEs tend to sweep aside cosmic rays, making it more difficult for cosmic rays to reach Earth. On the other hand, low solar activity allows an extra dose of cosmic rays to reach our planet. Indeed, the ongoing increase in cosmic ray intensity is probably due to a decline in the solar cycle.
INTENSIFYING COSMIC RAYS: For the past year, neutron monitors around the Arctic Circle have sensed an increasing intensity of cosmic rays. Polar latitudes are a good place to make such measurements, because Earth's magnetic field funnels and concentrates cosmic radiation there. Turns out, Earth's poles aren't the only place cosmic rays are intensifying. Spaceweather.com and the students of Earth to Sky Calculus have been launching helium balloons to the stratosphere to measure radiation, and they find the same trend over California:
In the plot, neutron monitor measurements from the University of Oulu Cosmic Ray Station are traced in red; gamma-ray/X-ray measurements over California are denoted in gray. The agreement between the two curves is remarkable. It means that the intensification of cosmic rays is making itself felt not only over the poles, but also over lower latitudes where Earth's magnetic field provides a greater degree of protection against deep space radiation.
Cosmic rays, which are accelerated toward Earth by distant supernova explosions and other violent events, are an important form of space weather. They can seed clouds, trigger lightning, and penetrate commercial airplanes. Indeed, our measurements show that someone flying back and forth across the continental USA, just once, can absorb as much ionizing cosmic radiation as 2 to 5 dental X-rays. Likewise, cosmic rays can affect mountain climbers, high-altitude drones, and astronauts onboard the International Space Station.
This type of radiation is modulated by solar activity. Solar storms and CMEs tend to sweep aside cosmic rays, making it more difficult for cosmic rays to reach Earth. On the other hand, low solar activity allows an extra dose of cosmic rays to reach our planet. Indeed, the ongoing increase in cosmic ray intensity is probably due to a decline in the solar cycle.