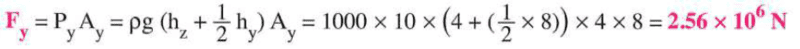Homework Help Overview
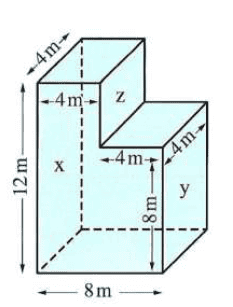
The discussion revolves around calculating the average force on the side walls of a container filled with fluid, specifically focusing on the pressure exerted at different heights within the fluid. The subject area includes fluid mechanics and pressure calculations.
Discussion Character
- Exploratory, Conceptual clarification, Assumption checking
Approaches and Questions Raised
- Participants are questioning the inclusion of specific terms in the force calculation, particularly the term related to pressure at different heights. There is a discussion about the nature of pressure in fluids and how it acts on surfaces. Some participants are exploring the implications of integrating pressure over varying heights.
Discussion Status
The discussion is ongoing, with participants clarifying concepts related to pressure and its effects on the container walls. Some guidance has been offered regarding the interpretation of pressure at different depths, but there is no explicit consensus on the correct approach or formula yet.
Contextual Notes
Participants are navigating through assumptions about pressure directionality and the effects of fluid weight on force calculations. There is mention of integration leading to different interpretations of the problem, indicating potential complexities in the setup.