SUMMARY
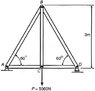
The discussion focuses on calculating nodal forces in a simple truss structure, specifically using the equations of static equilibrium. The forces at node A were determined to be 2500 N horizontally and 2500 N vertically, while nodes B and C each experienced a vertical force of 5000 N with no horizontal components. The net forces at each node must sum to zero in both x and y directions, and the solution emphasizes starting with end support reactions before analyzing simpler joints. The calculations align with results obtained through graphical truss analysis, enhancing confidence in solving truss problems.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium principles
- Familiarity with truss analysis techniques
- Knowledge of vector components in physics
- Ability to apply trigonometric functions in engineering contexts
NEXT STEPS
- Study the method of joints in truss analysis
- Learn about graphical methods for truss analysis
- Explore the use of software tools for structural analysis, such as SAP2000
- Investigate the effects of different loading conditions on truss stability
USEFUL FOR
Students in civil or structural engineering, professionals involved in structural design, and anyone seeking to enhance their understanding of truss mechanics and force calculations.