- #1
radaballer
- 86
- 0
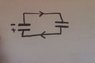
I want to calculate the total energy lost when a charged capacitor discharges to a neutral capacitor. It is my understanding that voltage will remain constant in the discharge, but current will decrease. What factors should be accounted for in any energy losses that would occur in this process?