- #1
Alexander Camargo
- 19
- 2
I need help to construct this source on mcnpx. I tried a lot of thing, but nothing worked. The source is a isotropic point source, but the beam is rectangular with dimensions of the same of scoring plane. The source is the standard mammography beam. Please, help.
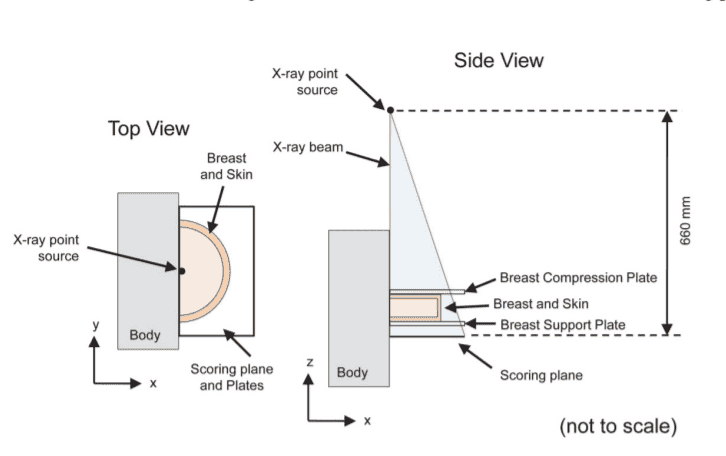
My parameters in use:
SDEF POS=0 0 66 ERG=d3 PAR=2 VEC=0 0 -1 DIR=d1 ext=d2 axs=1 0 0
SI1 -1 0.992733782 1 $ histogram for cosine bin limits
SP1 0 0.996366891 0.003633109 $ frac. solid angle for each bin
SB1 0 0 1 $ source bias for each bin
si2 0 .03 $ Focal spot with 3mm
sp2 -21 1
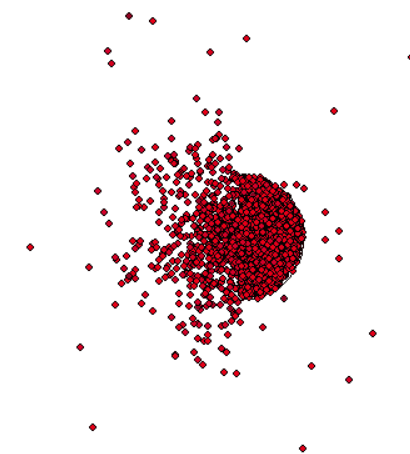
My parameters in use:
SDEF POS=0 0 66 ERG=d3 PAR=2 VEC=0 0 -1 DIR=d1 ext=d2 axs=1 0 0
SI1 -1 0.992733782 1 $ histogram for cosine bin limits
SP1 0 0.996366891 0.003633109 $ frac. solid angle for each bin
SB1 0 0 1 $ source bias for each bin
si2 0 .03 $ Focal spot with 3mm
sp2 -21 1