- #1
Selectron09
- 20
- 3
Homework Statement
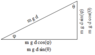
I don’t understand why this would relate to cosine and not sine, if gravity is often assiciated in the up and down part of a free body diagram.
Homework Equations
Wg=mgdcos(theta)[/B]The Attempt at a Solution
Is it because it would depend on your reference frame?