mwaso
- 11
- 0
Homework Statement
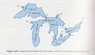
The idea of the problem is to find out how long it would take to flush the Great Lakes of pollution. They're set up as a series of five tanks and you are given inflow rates of clean water, inflow rates from the other tanks, and outflow rates. See attached figure.
Homework Equations
dA/dt=ratein-rate out where A is the amount of pollution at time t
The Attempt at a Solution
first I wrote equations for each lake. rather than using A as my variable, I used the first letter of each lake (with n for Ontario) to stand for the amount of pollution in the given lake at time t. this gives...
ds/dt=-15s/2900
dm/dt= -38m/1180
dh/dt=15s/2900 + 38m/1180 - 68h/850
de/dt=68h/850 - 85e/116
dn/dt=85e/116 - 99n/393
rearranging and pulling out the differential operator leads to the following system
(D + 38/1180)[m]=0
(D - 68/850)[h] + 38m/1180 - 15s/2900=0
(D + 15/2900)
(D + 85/116)[e] -68h/850=0
(D + 99/393)[n] - 85e/116=0
and there you have it. A system of five equations with five variables. It seems like it should be fairly straightforward to solve from here, but I can't figure out what to do next. I'm stuck!
Attachments
Last edited: