- #1
- 908
- 572
- TL;DR Summary
- Example of DiracDelta from the Wolfram Language help doesn't seem to work, at least on Wolfram Cloud.
The page on the Wolfram function DiracDelta has this example:
It's the first example under Examples > Basic Examples. When I run it in Wolfram Cloud, it says "Invalid integration variable or limit(s) ..."
and shows this result:
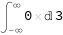
What's going wrong?
Edit: here's a screenshot:
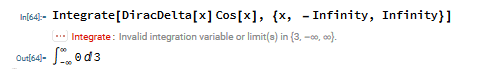
Code:
Integrate[DiracDelta[x] Cos[x], {x, -Infinity, Infinity}]and shows this result:
What's going wrong?
Edit: here's a screenshot: