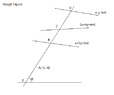
SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on finding the equation of a line passing through the point \(A(-5,-4)\) that intersects three given lines at points \(B\), \(C\), and \(D\). The relationship between the distances from point \(A\) to these intersection points is defined by the equation \(\left(\frac{15}{AB}\right)^2 + \left(\frac{10}{AC}\right)^2 = \left(\frac{6}{AD}\right) ^2\). The method involves calculating the gradient \(m\) of the line using the coordinates of points \(B\), \(C\), and \(D\) derived from the equations of the intersecting lines. Ultimately, the value of \(m\) allows for the determination of the line's equation.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of linear equations and gradients
- Familiarity with coordinate geometry
- Ability to manipulate algebraic equations
- Knowledge of distance formulas in geometry
NEXT STEPS
- Explore methods for solving systems of linear equations
- Learn about the distance formula in coordinate geometry
- Study the concept of gradients and slopes of lines
- Investigate the application of the Pythagorean theorem in geometric contexts
USEFUL FOR
Students and educators in mathematics, particularly those focusing on geometry and algebra, as well as anyone interested in solving problems involving lines and distances in a coordinate plane.