- #1
uzair_ha91
- 92
- 0
I just read this article (http://physics.bu.edu/~duffy/PY106/Potential.html).
I am stuck on just one line where it says that potential energy is in negative...please read this and explain...
"""""An example : Ionization energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom
In the Bohr model of a hydrogen atom, the electron, if it is in the ground state, orbits the proton at a distance of r = 5.29 x 10-11 m. Note that the Bohr model, the idea of electrons as tiny balls orbiting the nucleus, is not a very good model of the atom. A better picture is one in which the electron is spread out around the nucleus in a cloud of varying density; however, the Bohr model does give the right answer for the ionization energy, the energy required to remove the electron from the atom.
The total energy is the sum of the electron's kinetic energy and the potential energy coming from the electron-proton interaction.
The kinetic energy is given by KE = 1/2 mv2.
This can be found by analyzing the force on the electron. This force is the Coulomb force; because the electron travels in a circular orbit, the acceleration will be the centripetal acceleration:
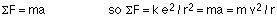
Note that the negative sign coming from the charge on the electron has been incorporated into the direction of the force in the equation above.
This gives m v2 = k e2 / r, so the kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 k e2 / r.
The potential energy, on the other hand, is PE = - k e2 / r. Note that the potential energy is twice as big as the kinetic energy, but negative. This relationship between the kinetic and potential energies is valid not just for electrons orbiting protons, but also in gravitational situations, such as a satellite orbiting the Earth.
The total energy is:
KE + PE = -1/2 ke2 / r = - 1/2 (8.99 x 109)(1.60 x 10-19) / 5.29 x 10-11
This works out to -2.18 x 10-18 J. This is usually stated in energy units of electron volts (eV). An eV is 1.60 x 10-19 J, so dividing by this gives an energy of -13.6 eV. To remove the electron from the atom, 13.6 eV must be put in; 13.6 eV is thus the ionization energy of a ground-state electron in hydrogen. """"""""
Please explain why P.E. is negative while K.E. is positive...
I am stuck on just one line where it says that potential energy is in negative...please read this and explain...
"""""An example : Ionization energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom
In the Bohr model of a hydrogen atom, the electron, if it is in the ground state, orbits the proton at a distance of r = 5.29 x 10-11 m. Note that the Bohr model, the idea of electrons as tiny balls orbiting the nucleus, is not a very good model of the atom. A better picture is one in which the electron is spread out around the nucleus in a cloud of varying density; however, the Bohr model does give the right answer for the ionization energy, the energy required to remove the electron from the atom.
The total energy is the sum of the electron's kinetic energy and the potential energy coming from the electron-proton interaction.
The kinetic energy is given by KE = 1/2 mv2.
This can be found by analyzing the force on the electron. This force is the Coulomb force; because the electron travels in a circular orbit, the acceleration will be the centripetal acceleration:
Note that the negative sign coming from the charge on the electron has been incorporated into the direction of the force in the equation above.
This gives m v2 = k e2 / r, so the kinetic energy is KE = 1/2 k e2 / r.
The potential energy, on the other hand, is PE = - k e2 / r. Note that the potential energy is twice as big as the kinetic energy, but negative. This relationship between the kinetic and potential energies is valid not just for electrons orbiting protons, but also in gravitational situations, such as a satellite orbiting the Earth.
The total energy is:
KE + PE = -1/2 ke2 / r = - 1/2 (8.99 x 109)(1.60 x 10-19) / 5.29 x 10-11
This works out to -2.18 x 10-18 J. This is usually stated in energy units of electron volts (eV). An eV is 1.60 x 10-19 J, so dividing by this gives an energy of -13.6 eV. To remove the electron from the atom, 13.6 eV must be put in; 13.6 eV is thus the ionization energy of a ground-state electron in hydrogen. """"""""
Please explain why P.E. is negative while K.E. is positive...
Last edited by a moderator: