Spongecake
- 11
- 0
Homework Statement
Figure shows a 50 Hz, high-voltage, transmission line. The relationships between the sending and receiving end voltages and currents are given by the complex ABCD equations:
where 'S' stands for sending-end and 'R' stands for receiving-end
(a) Given the parameter values in TABLE C and an open-circuit received voltage measured as 88.9 kV, calculate the values of
(b) If the line is modeled by the T-circuit of FIGURE 3(b), see if you can estimate the primary line coefficients R, L, G and C. The line is 50 km long.
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
Regarding part b) this is what I have at the moment but not sure I am doing it correctly.
A= 0.8698+J0.03542 B= 47.94+J180.8 C= 0+J0.001349 D= 0.8698+J0.03542
This means that A and D a symmetrical A=D.
I don't really know where to go from here as I have looked at other posts on this question and they don't seem to make much sense due to lots of people asking several different questions.
Attachments
-
 transmission line.jpg12.7 KB · Views: 506
transmission line.jpg12.7 KB · Views: 506 -
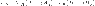 mimetex-cgi-20v_s-v_r-a_1-ja_2-i_r-b_1-jb_2-gif.gif1 KB · Views: 828
mimetex-cgi-20v_s-v_r-a_1-ja_2-i_r-b_1-jb_2-gif.gif1 KB · Views: 828 -
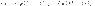 mimetex-cgi-20i_s-v_r-c_1-jc_2-i_r-d_1-jd_2-gif.gif1 KB · Views: 592
mimetex-cgi-20i_s-v_r-c_1-jc_2-i_r-d_1-jd_2-gif.gif1 KB · Views: 592 -
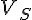 mimetex-cgi-20v_s-gif.gif206 bytes · Views: 625
mimetex-cgi-20v_s-gif.gif206 bytes · Views: 625 -
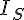 mimetex-cgi-20i_s-gif.gif179 bytes · Views: 615
mimetex-cgi-20i_s-gif.gif179 bytes · Views: 615 -
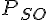 mimetex-cgi-20p_-so-gif.gif251 bytes · Views: 623
mimetex-cgi-20p_-so-gif.gif251 bytes · Views: 623 -
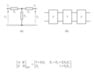 formulae-png.png5 KB · Views: 610
formulae-png.png5 KB · Views: 610