Discussion Overview
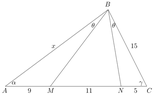
The discussion revolves around finding the length of side AB in triangle ABC, given specific lengths and angles involving points M and N on side AC. The problem involves geometric relationships and potentially the application of the sine rule and tangent functions.
Discussion Character
- Mathematical reasoning
- Technical explanation
- Debate/contested
Main Points Raised
- One participant suggests a proportional relationship between segments, proposing that x/9 = 15/5, but questions whether this is valid.
- Another participant counters that triangles ABM and BNC are not similar, indicating that the solution is not straightforward.
- A further reply questions the relevance of the length MN = 11 in the context of the problem.
- One participant presents a detailed approach using the sine rule in triangles BNC, BMA, and ABC, leading to a derived relationship between angles and sides, ultimately suggesting a calculated value for x.
- Another participant proposes an alternative method using coordinates and tangent relationships, suggesting a different approach to solving for AB.
Areas of Agreement / Disagreement
Participants express differing views on the similarity of triangles involved and the methods to solve for side AB. There is no consensus on the best approach or the validity of the initial proportional reasoning.
Contextual Notes
Some participants note the complexity of the relationships and the need for careful consideration of angles and triangle properties. The discussion reflects various assumptions and methods without resolving them.