- #1
Luke Tan
- 29
- 2
- TL;DR Summary
- How do i solve this ODE?
When reading through Shankar's Principles of Quantum Mechanics, I came across this ODE
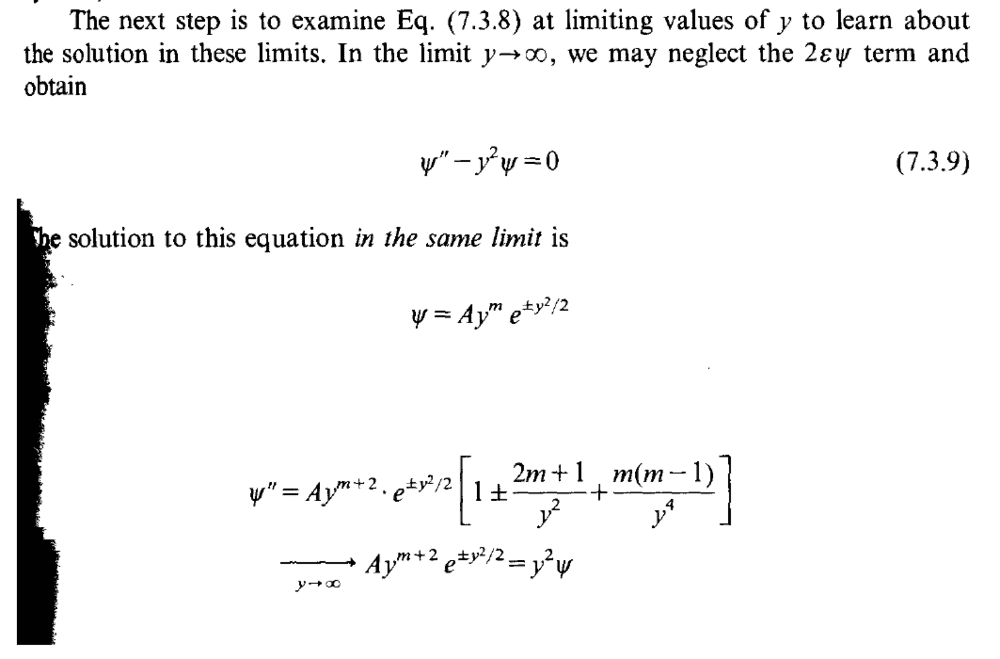
[tex]\psi''-y^2\psi=0[/tex]
solved in the limit where y tends to infinity.
I have tried separating variables and attempted to use an integrating factor to solve this in the general case before taking the limit, but they didn't work.
I also tried to guess a solution of the form [itex]e^{f(y)}[/itex], and it quickly became clear that [tex]f(y)=\frac{y^2}{2}[/tex], but it feels like my guess is unmotivated and i didn't get the [itex]y^m[/itex] term since i didn't guess it would be there.
Is there any general method for this kind of ODE?
[tex]\psi''-y^2\psi=0[/tex]
solved in the limit where y tends to infinity.
I have tried separating variables and attempted to use an integrating factor to solve this in the general case before taking the limit, but they didn't work.
I also tried to guess a solution of the form [itex]e^{f(y)}[/itex], and it quickly became clear that [tex]f(y)=\frac{y^2}{2}[/tex], but it feels like my guess is unmotivated and i didn't get the [itex]y^m[/itex] term since i didn't guess it would be there.
Is there any general method for this kind of ODE?