SUMMARY
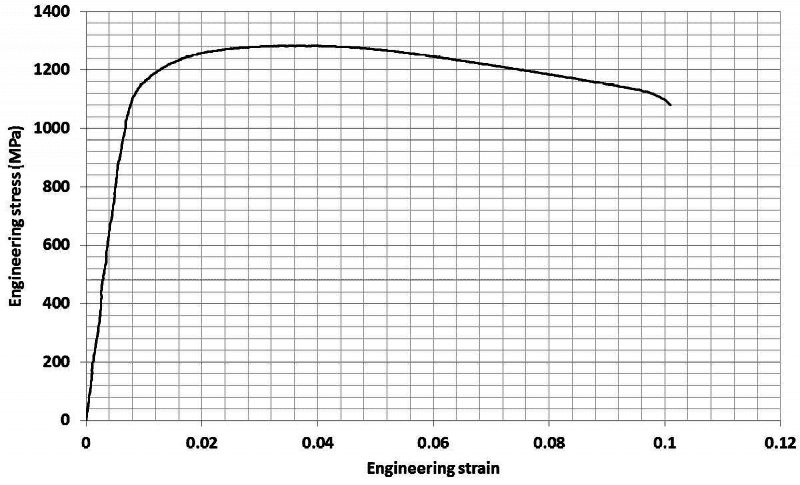
This discussion focuses on calculating elastic modulus, yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation from stress-strain curves. The elastic modulus is determined using the formula E = stress/strain, specifically from the linear region of the curve, typically measured from 0 to 0.02 strain for materials like aluminum. Yield and tensile strengths can be identified from the curve, while uniform and total elongation require understanding the original and final lengths of the material. The 2% rule is highlighted as a method for estimating Young's modulus in non-linear materials like aluminum.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of stress-strain curves
- Knowledge of Young’s modulus and its calculation
- Familiarity with yield strength and tensile strength concepts
- Basic grasp of engineering strain definitions
NEXT STEPS
- Research the calculation of yield strength from stress-strain curves
- Study the differences between uniform and total elongation
- Learn about the application of the 2% rule for estimating Young's modulus in materials
- Explore the characteristics of stress-strain curves for different materials, such as steel and aluminum
USEFUL FOR
Materials engineers, mechanical engineers, and students studying material properties will benefit from this discussion, particularly those involved in analyzing stress-strain behaviors and material strength calculations.