SUMMARY
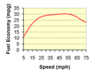
This discussion focuses on calculating the power required by gas vehicles, specifically using a Honda Civic as an example. Key factors include vehicle mass (2000 lbs), fuel efficiency (30 MPG), and the impact of speed on power requirements. The discussion highlights that air resistance and tire rolling friction are the primary kinetic energy losses, with calculations indicating that approximately 55 MJ of energy is needed for a gas vehicle to travel 50 miles. Comparisons between electric and gas power reveal that while electric vehicles may appear more efficient, significant energy losses occur during electricity generation and battery charging.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of vehicle dynamics and power calculations
- Familiarity with energy efficiency metrics (e.g., MPG, MJ)
- Knowledge of aerodynamic principles (e.g., Bernoulli's equation)
- Basic concepts of electric vehicle battery technology
NEXT STEPS
- Research the Bernoulli equation and its application in automotive aerodynamics
- Learn about tire rolling resistance coefficients and their impact on vehicle efficiency
- Explore energy conversion losses in electric vehicle charging systems
- Investigate advancements in supercapacitor technology for electric vehicles
USEFUL FOR
Automotive engineers, energy analysts, and anyone interested in comparing the efficiency and power requirements of gas versus electric vehicles.