SUMMARY
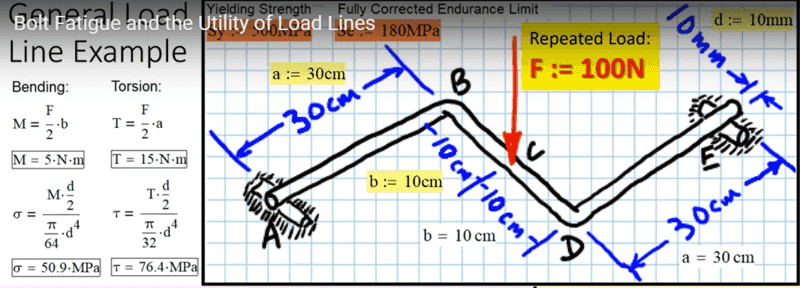
The discussion centers on calculating torsion in mechanical systems, specifically addressing the formula used to determine torsion at point C. Participants clarify that the force F is divided by 2 to obtain the magnitude of the reaction forces at support points A and E, while the distance 'a' remains unchanged. This understanding is crucial for accurately applying the principles of torsion in engineering calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Basic understanding of torsion in mechanics
- Familiarity with reaction forces in static equilibrium
- Knowledge of force distribution in structural analysis
- Concept of moment arms in torque calculations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of static equilibrium in mechanical systems
- Learn about calculating reaction forces in beams and frames
- Explore the concept of torsion and its applications in engineering
- Investigate the relationship between force, distance, and torque
USEFUL FOR
Mechanical engineers, physics students, and anyone involved in structural analysis or torsion calculations will benefit from this discussion.