You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
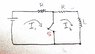
Independence of Currents in Inductor-Switch Circuit
AI Thread Summary
In an inductor-switch circuit, closing the switch creates a scenario where currents I1 and I2 may appear independent due to the zero voltage across the short circuit. However, the discussion highlights that the two currents are not entirely independent because they flow through the same circuit elements, which creates a dependency. The presence of shared components means that changes in one current can affect the other. This interconnectedness raises questions about the nature of current flow and dependency in circuit analysis. Ultimately, while the currents may seem independent at first glance, their interaction through shared elements indicates a level of dependence.
Engineering news on Phys.org
- 19,335
- 15,460
Well, what do you think would make them independent or dependent?
abdullah khaled
- 6
- 0
- 19,335
- 15,460
How about the fact that they both flow through the same element? Does that not connect them in some way? Or put another way, are the two currents totally isolated from each other?
I recently made a basic simulation of wire antennas and I am not sure if the near field in my simulation is modeled correctly. One of the things that worry me is the fact that sometimes I see in my simulation "movements" in the near field that seems to be faster than the speed of wave propagation I defined (the speed of light in the simulation).
Specifically I see "nodes" of low amplitude in the E field that are quickly "emitted" from the antenna and then slow down as they approach the far...
Hello dear reader,
a brief introduction:
Some 4 years ago someone started developing health related issues, apparently due to exposure to RF & ELF related frequencies and/or fields (Magnetic). This is currently becoming known as EHS. (Electromagnetic hypersensitivity is a claimed sensitivity to electromagnetic fields, to which adverse symptoms are attributed.) She experiences a deep burning sensation throughout her entire body, leaving her in pain and exhausted after a pulse has occurred...
Similar threads
- Replies
- 19
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 906
- Replies
- 30
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 3
- Views
- 803
- Replies
- 5
- Views
- 1K
- Replies
- 17
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 14
- Views
- 4K
- Replies
- 4
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 7
- Views
- 2K
- Replies
- 37
- Views
- 2K
Hot Threads
-
Spain’s power outage
- Started by Guineafowl
- Replies: 59
- Electrical Engineering
-
PVC Induction Heating Coil Design (early thoughts)
- Started by RickDelta
- Replies: 51
- Electrical Engineering
-
Using Latex Code for Circuit Diagrams
- Started by neilparker62
- Replies: 25
- Electrical Engineering
-
What is the difference between a switch leg and a hot leg?
- Started by sevensages
- Replies: 37
- Electrical Engineering
Recent Insights
-
Insights Quantum Entanglement is a Kinematic Fact, not a Dynamical Effect
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 7
- Quantum Physics
-
Insights What Exactly is Dirac’s Delta Function? - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- General Math
-
Insights Relativator (Circular Slide-Rule): Simulated with Desmos - Insight
- Started by Greg Bernhardt
- Replies: 0
- Special and General Relativity
-
Insights Fixing Things Which Can Go Wrong With Complex Numbers
- Started by PAllen
- Replies: 7
- General Math
-
Insights Fermat's Last Theorem
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 78
- General Math
-
Insights Why Vector Spaces Explain The World: A Historical Perspective
- Started by fresh_42
- Replies: 0
- General Math