SUMMARY
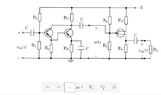
The discussion centers on the input and output impedance of a circuit involving multiple transistors, specifically focusing on how the output impedance of the first amplifier stage (Zout1) and the input impedance of the second stage (Zin2) interact. The input impedance of the second amplifier stage loads the output drive of the first stage, but this does not alter Zout1. The analysis involves using the Hybrid pi model for bipolar transistors, where the input impedance is calculated as Rb + (Rpi + Re) * (Beta + 1), typically yielding values between 1K-10K. The output impedance is dominated by Ro, which ranges from 100K-10M, affecting the overall circuit dynamics.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of small signal models in transistor circuits
- Familiarity with Hybrid pi model for bipolar transistors
- Knowledge of circuit analysis techniques, including KVL and load resistance calculations
- Experience with SPICE for circuit simulation
NEXT STEPS
- Study the Hybrid pi model for bipolar transistors in detail
- Learn about small signal analysis techniques for multi-stage amplifiers
- Explore SPICE simulation for analyzing interstage impedance matching
- Research DC biasing techniques in transistor circuits
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying amplifier design and transistor circuit analysis will benefit from this discussion.