Mr. Heretic
- 16
- 0
Greetings and salutations.
Today I bring with me interesting phenomena, which I managed to reproduce and photograph in detail.
I noticed one when I was enjoying my ~300mW 532nm laser in a dark room, if I reflect the beam off a regular plane mirror with a small angle, it projects 2 separate interference(?) patterns onto an opposing surface, becoming noticeable at about 8 degrees and highly visible at around 2, based on distance measurements and trig.
Both are pictured in the attachments, though I've had to scale and reduce quality woefully to meet the strict filesize guidelines.
I advise downloading the 100% size and quality version for closer inspection from: https://picasaweb.google.com/lh/photo/SLeE64Xo8-6n0dO8JC109p1FDvtn5lS-MCahxU362JM?feat=directlink
Only place I could find to host a 15.3mb image, use the download option on the top left.
Note that the main/large pattern is not centered at the point the beam has reflected to, based on attempts to give the laser only vertical, horizontal and angular shifts: it is affected equally (to the beam point) in the former two, but half as drastically in the angular shifts, which is to say reflected at half the angle.
A second, much smaller pattern can be seen at the actual point of the laser beam, which was only revealed in the photograph, the point is too bright to look at directly so it's possibly an artifact of the camera/lens.
I have two ideas on what could be causing it, but certainly nothing solid:
1. Markings/grit/fingerprints on the mirror surface potentially acting like a diffraction grating, though it's not like any light diffraction I've seen.
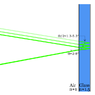
2. Partial reflection within the glass of the mirror, creating secondary out-of-phase beams at proximity to the original. (diagram included, attachment 3)
Any ideas?
Today I bring with me interesting phenomena, which I managed to reproduce and photograph in detail.
I noticed one when I was enjoying my ~300mW 532nm laser in a dark room, if I reflect the beam off a regular plane mirror with a small angle, it projects 2 separate interference(?) patterns onto an opposing surface, becoming noticeable at about 8 degrees and highly visible at around 2, based on distance measurements and trig.
Both are pictured in the attachments, though I've had to scale and reduce quality woefully to meet the strict filesize guidelines.
I advise downloading the 100% size and quality version for closer inspection from: https://picasaweb.google.com/lh/photo/SLeE64Xo8-6n0dO8JC109p1FDvtn5lS-MCahxU362JM?feat=directlink
Only place I could find to host a 15.3mb image, use the download option on the top left.
Note that the main/large pattern is not centered at the point the beam has reflected to, based on attempts to give the laser only vertical, horizontal and angular shifts: it is affected equally (to the beam point) in the former two, but half as drastically in the angular shifts, which is to say reflected at half the angle.
A second, much smaller pattern can be seen at the actual point of the laser beam, which was only revealed in the photograph, the point is too bright to look at directly so it's possibly an artifact of the camera/lens.
I have two ideas on what could be causing it, but certainly nothing solid:
1. Markings/grit/fingerprints on the mirror surface potentially acting like a diffraction grating, though it's not like any light diffraction I've seen.
2. Partial reflection within the glass of the mirror, creating secondary out-of-phase beams at proximity to the original. (diagram included, attachment 3)
Any ideas?
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: