- #1
quietrain
- 655
- 2
the atomic nucleus mass is given by
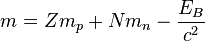
but why is it a minus away of binding energy / c2 = mass of the empty parts of the nucleus?
shouldn't it be a plus?
mass of nucleus = proton mass + neutron mass + mass of empty parts of the nucleus?
but why is it a minus away of binding energy / c2 = mass of the empty parts of the nucleus?
shouldn't it be a plus?
mass of nucleus = proton mass + neutron mass + mass of empty parts of the nucleus?