SUMMARY
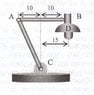
The discussion centers on calculating the weight of rod AC in a system involving rods AB and D, with specific weights of 4[N] and 10[N] respectively, and a moment at joint C of 1.8[Nm]. The correct calculation shows that the weight of rod AC should be 6[N], contrary to the initial calculation of 66[N]. Participants emphasize the importance of correctly summing individual contributions to the moment at point C, rather than incorrectly adding the total moment to individual forces.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of static equilibrium and moments in physics
- Familiarity with torque calculations and their units (N·m)
- Ability to interpret and create free body diagrams
- Knowledge of basic algebra for solving equations
NEXT STEPS
- Study the principles of static equilibrium in mechanics
- Learn how to construct and analyze free body diagrams
- Explore the concept of torque and its applications in engineering
- Review problem-solving techniques for statics problems in physics
USEFUL FOR
Students in physics or engineering courses, educators teaching mechanics, and professionals involved in structural analysis or design.