SUMMARY
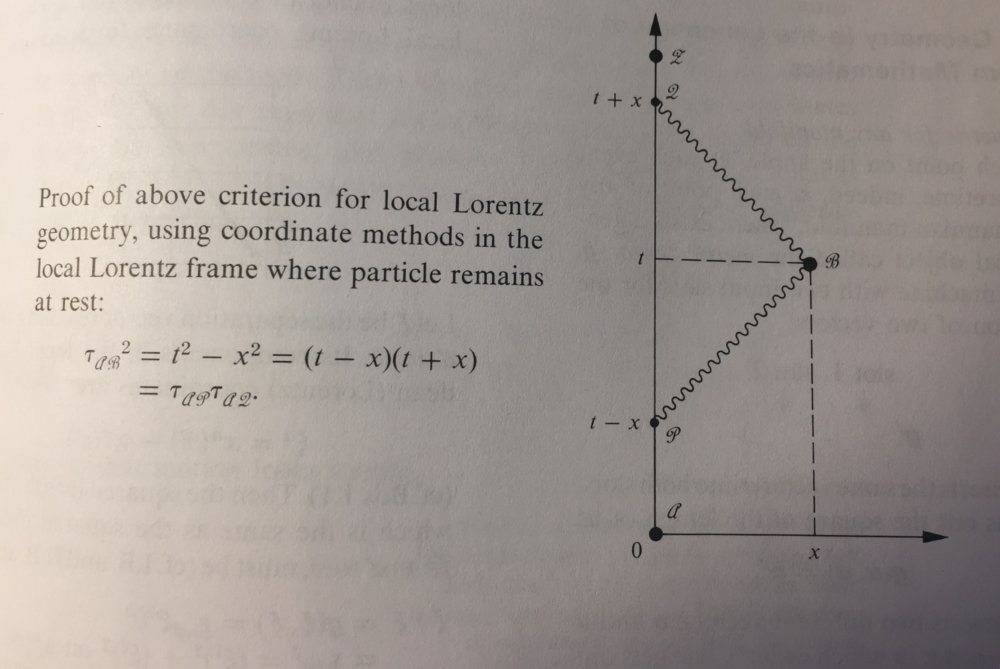
The proper time in Lorentz geometry is defined using the formula t² - x² rather than t² + x² due to the nature of Minkowski geometry, which differs fundamentally from Euclidean geometry. The Lorentz transformations preserve the invariant interval Δt² - Δx², making it the physically significant quantity in relativity. This invariant interval corresponds to the proper time between two events in spacetime, which is crucial for understanding the behavior of objects moving at relativistic speeds. The discussion emphasizes the importance of Minkowski diagrams for visualizing these relationships, despite their Euclidean representation limitations.
PREREQUISITES
- Minkowski geometry fundamentals
- Lorentz transformations and their implications
- Invariant intervals in special relativity
- Understanding of spacetime diagrams
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of Lorentz transformations in detail
- Explore Minkowski diagrams and their applications in relativity
- Learn about invariant intervals and their significance in physics
- Examine the implications of the speed of light as an invariant speed in various frames
USEFUL FOR
Students of physics, particularly those studying special relativity, mathematicians interested in geometry, and educators looking to explain the concepts of spacetime and Lorentz transformations.