SUMMARY
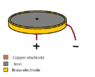
The discussion focuses on the magnetic field generated by a DC current flowing between two electrodes through an iron disk, with a radius of 2.54 mm and a height of 1 cm. Participants emphasize the importance of visualizing the current distribution, which resembles bicycle spokes, and the resulting magnetic field. They reference the right-hand rule and suggest using computational methods to analyze the magnetic field, particularly through the use of elliptic integrals. The complexity of the problem is acknowledged, indicating that the magnetic field's behavior is non-trivial and requires careful consideration of the geometry and material properties.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of DC current and its flow in conductive materials
- Familiarity with the right-hand rule for determining magnetic field direction
- Knowledge of magnetic field concepts, including magnetic pole theory
- Basic understanding of elliptic integrals and their application in magnetic field calculations
NEXT STEPS
- Research computational methods for magnetic field analysis, focusing on elliptic integrals
- Learn about the Biot-Savart law and its application in calculating magnetic fields from current distributions
- Explore the concept of magnetization in materials, particularly in iron
- Investigate numerical methods for solving complex magnetic field problems in conductive geometries
USEFUL FOR
Physics students, electrical engineers, and anyone interested in understanding the magnetic fields generated by current-carrying conductors, particularly in complex geometries like disks.