SUMMARY
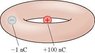
The net electric flux through a torus can be calculated using Gauss's law, which states that the net flux is equal to the enclosed charge divided by the permittivity of free space. In this discussion, the enclosed charge is specified as -1 nC. The formula for net flux is given by net flux = E * A, where E is the electric field and A is the area. The challenge arises from the lack of radius information needed to determine the area of the torus.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of Gauss's law in electromagnetism
- Familiarity with electric flux concepts
- Basic knowledge of charge units, specifically nanocoulombs (nC)
- Ability to calculate area for geometric shapes, particularly toroidal shapes
NEXT STEPS
- Review Gauss's law and its applications in electrostatics
- Learn how to calculate the area of a torus
- Explore electric field calculations for closed surfaces
- Study the relationship between enclosed charge and electric flux
USEFUL FOR
Students studying electromagnetism, physics educators, and anyone preparing for exams involving electric flux calculations.