evceteri
- 1
- 0
Hi, I'm reading Chapter 2-II of of Duderstadt & Hamilton's "Nuclear Reactor analysis". In the section "Differential scattering cross sections with upscattering" it is discussed the situation in which neutrons suffers elastic scattering collisions in a hydrogen gas at finite temperature T and the nuclei are in motion with a Maxwell - Boltzmann velocity distribution.
For this case they cite the scattering probability as given by
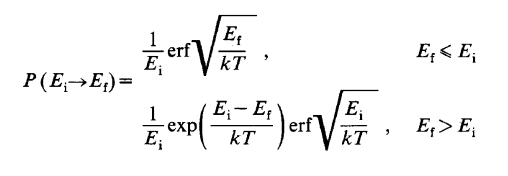
where
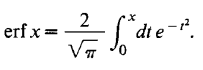
Then they plot the probability distribution for some incident neutron energies:
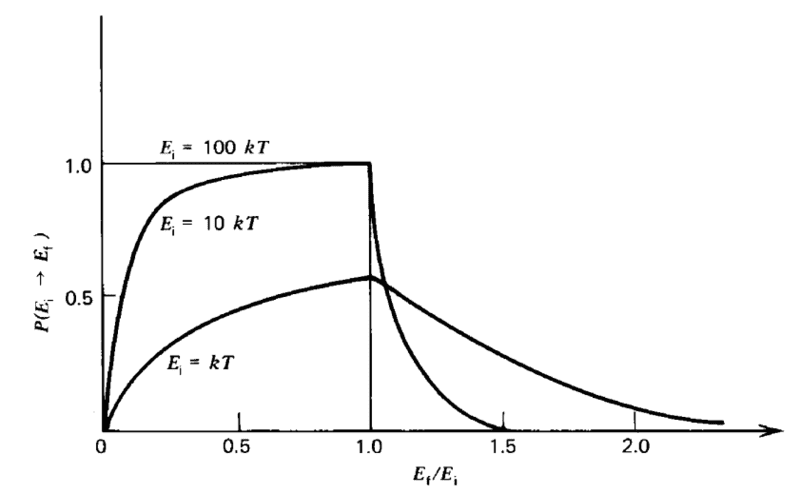
I've been trying to reproduce this plot but I just don't seem to understand how.
So, for example, if ##E_i = kT## and ##E_f/E_i = 1.0 ## then ##E_f = kT## and $$P(E_i \rightarrow E_f) = \frac {1} { kT} erf \sqrt { \frac {kT} {kT}} = \frac {0.84} {kT}$$.
I'm not sure what I'm supposed to do next, as the expected result in the plot is about 0.5. I know ##P(E_i \rightarrow E_f)## is a probability distribution so in order to get rid of the ##kT## I need to integrate but from where to where?
Can you help me figure it out?
For this case they cite the scattering probability as given by
where
Then they plot the probability distribution for some incident neutron energies:
I've been trying to reproduce this plot but I just don't seem to understand how.
So, for example, if ##E_i = kT## and ##E_f/E_i = 1.0 ## then ##E_f = kT## and $$P(E_i \rightarrow E_f) = \frac {1} { kT} erf \sqrt { \frac {kT} {kT}} = \frac {0.84} {kT}$$.
I'm not sure what I'm supposed to do next, as the expected result in the plot is about 0.5. I know ##P(E_i \rightarrow E_f)## is a probability distribution so in order to get rid of the ##kT## I need to integrate but from where to where?
Can you help me figure it out?