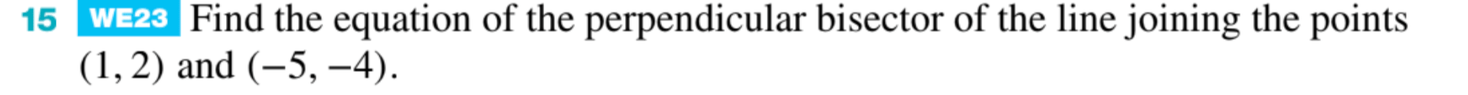SUMMARY
The discussion focuses on the concept of the perpendicular bisector in geometry, specifically how to derive its equation. The slope of the line connecting the points (1, 2) and (-5, -4) is calculated as 1, leading to a perpendicular slope of -1. The midpoint between the two points is determined to be (-2, 3), which serves as the point through which the perpendicular bisector passes. The equation of the line through (-2, 3) with a slope of -1 is derived from these calculations.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of slope calculation in coordinate geometry
- Knowledge of the midpoint formula
- Familiarity with the concept of perpendicular lines
- Ability to derive the equation of a line from a point and slope
NEXT STEPS
- Study the derivation of the equation of a line using point-slope form
- Explore the properties of perpendicular lines in Euclidean geometry
- Learn about the applications of perpendicular bisectors in triangle geometry
- Investigate the relationship between slopes and angles in coordinate systems
USEFUL FOR
Students of geometry, mathematics educators, and anyone looking to deepen their understanding of line equations and geometric properties.