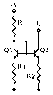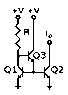SUMMARY
The discussion centers on the necessity of emitter resistors (R1 and R2) in current mirror circuits to enhance output resistance and mitigate the early effect. By increasing effective output impedance, these resistors minimize the variation in output current (I) due to changes in output voltage (V), thereby achieving a more stable current source. Additionally, the use of cascode transistors (Q2 and Q3) helps equalize collector voltages, improving thermal balance and preventing thermal runaway in high-current applications. The accurate current balance is primarily maintained by Q1 and Q2, while other components support their function.
PREREQUISITES
- Understanding of current mirror circuits
- Familiarity with the early effect in transistors
- Knowledge of thermal management in electronic circuits
- Basic principles of transistor operation and biasing
NEXT STEPS
- Research the Wilson current mirror design and its improvements
- Learn about thermal runaway prevention techniques in transistor circuits
- Explore the role of cascode configurations in enhancing output impedance
- Study the impact of emitter resistors on linearity in current sources
USEFUL FOR
Electrical engineers, circuit designers, and students studying analog electronics who are interested in improving the performance and stability of current mirror circuits.