- #1
fldk31
- 5
- 0
< Mentor Note -- thread moved to HH from the technical physics forums, so no HH Template is shown >
Could anyone please correct me if I have any mistake in the following question? It's very important for me to know if I am doing it correctly.
1)
"Michelle, a technician at a spring manufacturing plant,wants to make determining spring constants for fun. She fires a 0.0100kg bullet at a 500.0g wooden block that is attached to a massless spring;the bullet is traveling at 1000m/s when it strikes the block.The bullet lodges inside the block and the combination compresses the spring by 0.200m before it stops.Determine the spring constant that the technician oils calculate for this spring?"
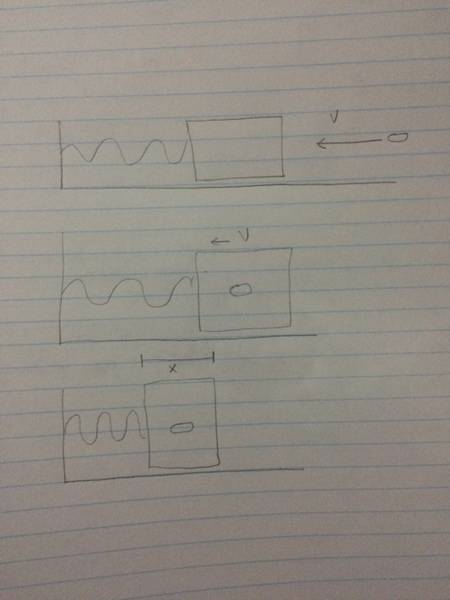
Solution:

Could anyone please correct me if I have any mistake in the following question? It's very important for me to know if I am doing it correctly.
1)
"Michelle, a technician at a spring manufacturing plant,wants to make determining spring constants for fun. She fires a 0.0100kg bullet at a 500.0g wooden block that is attached to a massless spring;the bullet is traveling at 1000m/s when it strikes the block.The bullet lodges inside the block and the combination compresses the spring by 0.200m before it stops.Determine the spring constant that the technician oils calculate for this spring?"
Solution: