hokhani
- 561
- 18
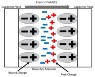
How does the force between the two opposite charge change if we place a substance (conductor, insulator, ...) between them? It seems that the force between the two charges doesn't change but the total force on each charge increases because of the superposition of the original field of the other charge and the extra electric field due to the induced charge on the substance. I would like to know if I am wrong.