- #1
mamech
- 4
- 0
Hello all
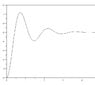
I know that the step response of a second order underdamped system is :
y(t) = 1 – (e^(-ζωn*t) / sin(θ))*sin(ωd*t + θ)
Where sin(θ)= sqrt(1-ζ^2) , ωd = sqrt(ωn^2 – ωn^2 * ζ^2 )
my question is: I can see on the simulation ωd and I can calculate it ,
but I want also to see the phase shift angle θ
I know already that θ= asin(sqrt(1-ζ^2) ) , but this is analytical, can I see and measure it on the graph?
thanks
I know that the step response of a second order underdamped system is :
y(t) = 1 – (e^(-ζωn*t) / sin(θ))*sin(ωd*t + θ)
Where sin(θ)= sqrt(1-ζ^2) , ωd = sqrt(ωn^2 – ωn^2 * ζ^2 )
my question is: I can see on the simulation ωd and I can calculate it ,
but I want also to see the phase shift angle θ
I know already that θ= asin(sqrt(1-ζ^2) ) , but this is analytical, can I see and measure it on the graph?
thanks