akaliuseheal
- 53
- 8
Homework Statement
Hello,
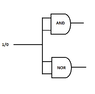
I have got input from comparator op amp which gives HIGH or LOW. Based upon that, one of two LEDs needs to light up. Two LEDs should't be ON at the same time.
Calculations are not needed, only the schematics.
Homework Equations
None
The Attempt at a Solution
I am not really familiar with the transistors, so I used logic gates.
Input = 1
AND 1 | NOR 0
Input = 0
AND 0 | NOR 1The use of logic gates should be avoided here, thus the use of transistors comes to my mind.