- #1
boogiepicker
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
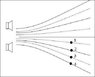
In the figure the two speakers are producing identical sound
waves. The solid lines represent constructive interference regions and the dashed lines represent destructive interference regions. The point labeled 1 is 662.15 m from the bottom speaker
and 742.9 m from the top speaker.
What is the wavelength of the sound waves
Homework Equations
v = f*lambda?, assuming v = 343 m/s
Pythagorean I believe has to be used but I'm not sure
The Attempt at a Solution
Attempted Pyth. to find distance between speakers, thinking this would be the PLD and then I'd be able to find the wavelength from there. This did not work.
Here's a picture: